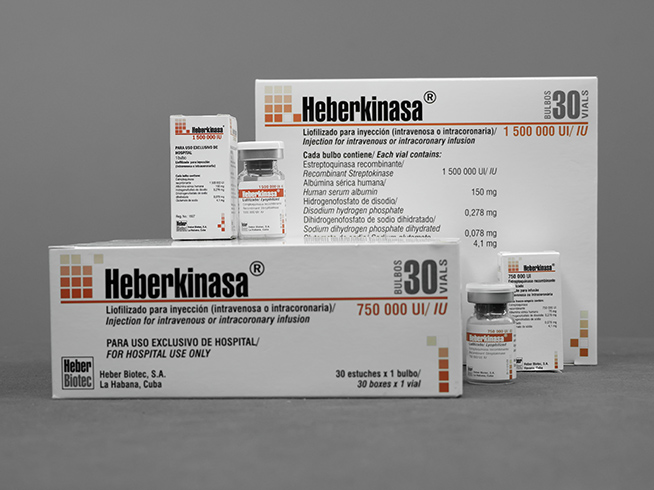
Heberkinasa®
Drug containing recombinant streptokinase, Heberkinasa® causes rapid lysis of the intracoronary thrombus and prevents ischemic necrosis of the myocardium. It improves ventricular function and limits the infarcted area. Restores venous circulation and prevents postphlebitic syndrome. It reduces the risk of pulmonary embolism and facilitates the rapid removal of the embolus.
Lyophilisate for intravenous, intracoronary infusion.
- 750,000 IU of recombinant human streptokinase
- 1 500,000 IU of recombinant human streptokinase
Recombinant human streptokinase 750,000 IU:
- Human serum albumin 75 mg
- Disodium hydrogen phosphate 0.278 mg
- Sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate 0.078 mg
- Sodium glutamate 4.1 mg
Recombinant human streptokinase 1,500,000 IU:
- Human serum albumin 150 mg
- Disodium hydrogen phosphate 0.278 mg
- Sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate 0.078 mg
- Sodium glutamate 4.1 mg
- Unreconstituted product: store at 2 to 8 °C
- Reconstituted product: store at 2 to 8 °C
- Acute myocardial infarction (AMI): the diagnosis must meet the following characteristics: patients of any age and sex, with pain in the anterior aspect of the chest or with a clinical picture suggestive of Myocardial ischemia, lasting more than 30 minutes, in the 12 hours preceding the start of treatment, accompanied by ST segment elevation on the electrocardiogram (ECG), of more than 1 mm, in 2 or more leads of the following: DI , DII, DIII, aVL, or aVF, or greater than 2 mm in two or more contiguous precordial leads, or bundle branch block.
- Deep vein thrombosis : lysis of thrombi is achieved in less than 72 hours and the appearance of postphlebitic syndrome is avoided in the long term.
- Thrombosis of permanent vascular access in patients with end-stage chronic kidney failure treated by periodic hemodialysis: the occluded arteriovenous fistula is recovered in 70% of treated patients.
- Dysfunction of heart valve prostheses due to thrombi: a 93.3% success rate was obtained, thus avoiding emergency surgery and reducing mortality.
- Pulmonary thromboembolism : a rapid recovery of cardiopulmonary function and vascular bed involvement is avoided.
Heberkinasa® is contraindicated in active bleeding, brain tumor or stroke, recent thoracic surgery, uncontrolled severe hypertension, dissecting aneurysm, cerebrovascular disease, subacute bacterial endocarditis, diabetic haemorrhagic retinopathy, recent major or minor trauma, sepsis at the site or near the thrombus, pregnancy and lactation. Also in active TB, kidney and / or liver failure.
It is contraindicated in the previous year to allergy to Heberkinasa® or with a history of allergy to Heberkinasa®.
The risk-benefit ratio should be evaluated in all clinical conditions where there is a risk of bleeding or where it would be difficult to control due to its location.
In patients aged 75 years and over, the risk of cerebral hemorrhage increases. It should be administered with great caution during the first 10 days after delivery due to the increased risk of bleeding. To minimize the risk of bleeding during thrombolytic therapy, the patient should be in bed, completely rest, avoiding any manipulation or movement, invasive procedures (biopsies) or intramuscular injections that are not essential. If heparin treatment was being carried out, it should be stopped. Resistance to thrombus lysis increases with age, so therapy should be carried out as soon as possible after clinical symptoms appear.
It should only be used under medical prescription. Treatment must be carried out by specialized personnel who have the necessary diagnostic facilities, as well as sufficient experience in thrombolytic therapy for AMI and other thrombotic diseases. This medicine can only be used until the expiration date indicated on the package.
After reconstitution, the solution can be stored between 2 and 8 ° C for 24 hours, without losing its activity. After this reconstitution period, the solution should not be used.
More than 3,000 patients were included in clinical trials with Heberkinasa®.
Proportion of patients with adverse events & gt; 1%:
| Adverse events | Frequency (%) | Adverse events | Frequency (%) | Adverse events | Frequency (%) |
| Arrhythmia | 47.8 | Others | 2.2 | Anaphylactic shock | 0.8 |
| Arterial hypotension | 24 | Myocardial reinfarction | 2.4 | Sudden death | 1.6 |
| Shaking chills | 12.7 | Nausea | 2.1 | Cardiogenic shock | 1.4 |
| Tremor | 12 | Stroke (AVE) | 1.1 | Bleeding | 3.2 |
| Angina pectoris | 10 | Hemorrhagic | 0.3 | Higher | 0.9 |
| Vomiting | 7.7 | Ischemic | 0.6 | Less | 2.3 |
| Fever | 7.3 | Undefined | 0.2 | Cardiac wall rupture (confirmed by necropsy) | 1.8 |
| Angioneurotic edema | 0.2 | Allergy | 3.2 | – | – |
Reconstitution and preparation of the medicine
The reconstitution and dilution of the drug, when it is going to be applied by intravenous infusion, is done with 5 mL of water for injection, trying to direct the liquid towards the walls of the bulb, which must be turned carefully to avoid the formation foam. The concentrated solution obtained is aseptically transferred to an infusion bottle of adequate volume, according to the needs of the patient. The most appropriate solutions are 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose. No other products should be added to this preparation.
- Acute myocardial infarction: The administration of Heberkinasa® should begin as soon as possible, never more than 12 hours after the onset of symptoms, intravenously or directly intracoronary. In systemic treatment, Heberkinase® will be administered once through a peripheral vein at a dose of 1,500,000 IU over the course of 60 minutes.
When the product is administered intracoronary via a coronary catheter, the application of a bolus of 20,000 IU is recommended, followed by an infusion of 2,000 to 4,000 IU per minute for 30 to 90 minutes.
- Deep vein thrombosis: For the application of Heberkinasa® in this type of affection, the intravenous route will be used by locoregional catheter in the maxillary-subclavian region or of the leg. When the thrombosis is in more than one location, the product will be applied to the most affected limb.
The application should be started as soon as possible after the onset of thrombosis. Patients will receive an initial dose of 250,000 IU within 30 minutes, and a maintenance dose of 100,000 IU per hour in continuous infusion for 24 to 72 hours depending on when the thrombus dissolves.
- Permanent vascular access thrombosis in patients with end-stage chronic renal failure treated by periodic hemodialysis: in this condition, Heberkinasa® will be administered directly into the arterial portion of the vascular access, by continuous infusion, 1 000 000 IU during a maximum period of 1 hour.
- Dysfunction of prosthetic heart valves due to thrombi: Through a peripheral vein of the upper limbs, 250,000 IU of Heberkinasa® are administered diluted in 100 mL of 5% dextrose or physiological saline solution, for 30 minutes. 100 000 IU / h should be continued for 72 hours or less if the thrombus lysis is achieved, clinically and imaging evidenced.
- Pulmonary thromboembolism : through 250,000 IU of Heberkinase ® diluted in 100 mL of 5% dextrose or physiological saline solution are administered to a peripheral vein of the upper limbs for 30 minutes. It should continue with 100,000 IU per hour for 72 hours or less, in case the lysis of the thrombus is achieved, evidenced by the clinic.
It increases the risk of severe bleeding in patients receiving corticosteroids, ethacrynic acid or non-acetylated salicylates. The use of antifibrinolytics inhibits the action of thrombolytics. Anticoagulants derived from coumarin or heparin increase the risk of bleeding. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), indomethacin, and phenylbutazone inhibit platelet aggregation and can cause gastrointestinal ulceration or bleeding.
However, in cases of myocardial infarction, the concomitant administration of ASA is indicated, since the beneficial effects of Heberkinasa® and ASA in terms of short-term lethality reduction are added.
The use of dipyridamole, piperacillin, valproic acid and ticarcillin also inhibit platelet aggregation with increased risk of bleeding.
Its use is not recommended in these situations.
Not applicable. It is a medical emergency with hospitalization of the patient. In any case, patients receiving Heberkinasa® should not drive vehicles or machinery.
An overdose of Heberkinasa® increases the risk of bleeding.