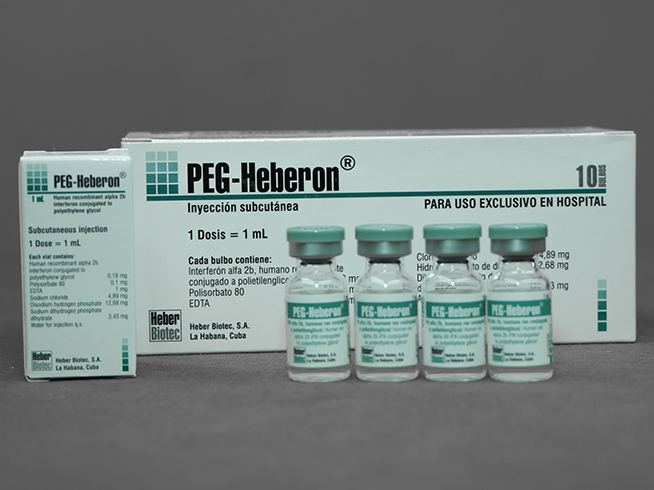
PEG-Heberon®
- Drug containing recombinant human interferon alpha 2b conjugated to polyethylene glycol for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and C
- With the use of PEG-Heberon® in combination with ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C, a sustained virological response of up to 40 % is achieved in patients with genotype 1 without previous treatment.
- After 6 months of treatment with PEG-Heberon®, viral replication remains undetectable.
- With the use of PEG-Heberon®, the control of the disease increases by 27 %, compared to conventional monotherapy with alpha interferon.
Solution for subcutaneous injection
Recombinant human interferon alpha 2b conjugated to polyethylene glycol 0.18 mg / mL
- Individual case
- Multiple box for 10 boxes with 10 bulbs
- Box of 10 bulbs
Each 1 mL contains 0.18 mg polyethylene glycol conjugated recombinant human interferon alpha 2b; polysorbate 80; EDTA; sodium chloride; disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4); sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate (NaH2PO4 x 2H2O); water for injection.
Store at 2 to 8 ° C. Do not freeze.
The use of PEG-Heberon® should be under medical prescription, in patients suffering from:
Chronic hepatitis C
Its use is aimed at obtaining a sustained virological response (SVR), defined as the non-recurrence of detectable viral particles in serum or plasma 6 months after the end of treatment. This criterion can be interpreted as remission or control of viral liver disease, and can be achieved even in individuals at risk of complications associated with liver cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma.
PEG-Heberon® is indicated in adult patients with liver cirrhosis and without liver cirrhosis, with compensated liver disease. This indication includes previously untreated individuals and nonresponsive or relapsing subjects after conventional interferon alpha monotherapy or its combination with ribavirin. It can also be used in patients co-infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or the hepatitis B virus (HBV), as well as in patients who have received a liver transplant.
The highest SVR percentages are achieved when using PEG-Heberon® in combination with ribavirin. This combined treatment is currently considered one of the most advantageous options for any patient diagnosed with chronic hepatitis C. Approximately 70 to 85% of patients infected with genotype 2 or 3 of the virus, who receive PEG-Heberon®, have SVR after 24 weeks of treatment. In contrast, SVR is only achieved in 50% of those infected with genotypes 1 or 4 treated for 48 weeks. Lower SVR percentages may occur in special subpopulations of patients, such as those coinfected with chronic hepatitis C and HIV.
The duration and dosing schedule of the combination PEG-Heberon® and ribavirin can be individualized per patient, based on virus genotype, baseline viral load, and virologic response at week 12 of treatment.
PEG-Heberon® monotherapy is essentially indicated in patients with intolerance to ribavirin or when ribavirin is contraindicated.
Chronic hepatitis B
The use of PEG-Heberon® is aimed at seroconversion to hepatitis B virus e antigen (HBeAg) or to achieve sustained virological response (SVR), defined as the non-recurrence of detectable viral particles in serum or plasma to 6 months after the end of the treatment. These criteria can be interpreted as remission or control of viral liver disease.
PEG-Heberon® is indicated as monotherapy for chronic hepatitis B with positive or negative HBsAg in adult patients with compensated liver disease, with evidence of viral replication, with high levels of alanine aminotransferase and proven necroinflammatory activity with or without fibrosis.
In both cases, the recommended duration of treatment is 48 weeks. It is possible to obtain 32% SVR and seroconversion for AgHBe, while in AgHBe negative patients 43% SVR is obtained.
The combination of PEG-Heberon® with antiviral drugs has not shown a significant increase in the therapeutic response in patients.
PEG-Heberon® is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to interferon alpha, to products derived from Escherichia coli, to polyethylene glycol (macrogol) or to any of the salts present in the preparation. It is also contraindicated in autoimmune hepatitis; severe liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis; history of severe heart disease, including unstable or uncontrolled heart disease within the past 6 months; lactation and hemoglobinopathies.
Its efficacy and toxicity in patients under 18 years of age have not been proven.
In associated administration with ribavirin, professional information on ribavirin should also be consulted.
Cardiovascular system: Although no direct cardiotoxic effect has been demonstrated, it is possible that some of the side effects (eg, fever, chills, general malaise) frequently associated with the administration of PEG-Heberon® exacerbate a previous cardiac disturbance.
Hematological system: PEG-Heberon® treatment has been associated with a decrease in total leukocyte count, absolute neutrophil count, and platelet count, which generally begin within the first 2 weeks of treatment. These decreases are reversible by reducing the dose or stopping therapy.
Because one of the toxic effects associated with the use of PEG-Heberon® may be leukopenia, extreme caution must be exercised when administering it to patients with myelosuppression.
In 15% of patients receiving combined treatment with ribavirin, a decrease in hemoglobin levels has been observed to values below 100 g / L.
Renal system: as the kidney is the site where the active principle is metabolized, care should be taken when using PEG-Heberon® in patients with compromised renal function, considering reducing the dose if necessary.
Psychiatry and central nervous system (CNS): serious CNS effects, specifically depression, suicidal ideation and suicide attempt have been observed in some patients during treatment with interferon alpha and even after treatment interruption, mainly during the follow-up period 6 months. Other CNS effects have been seen with alpha interferons, including aggressive behavior (sometimes directed toward other people), confusion, and altered mental status. Patients should be closely monitored for any signs or symptoms of psychiatric disorders. If these symptoms appear, the physician must take into account the potential severity of these adverse reactions and must consider the need for appropriate therapeutic treatment. If psychiatric symptoms persist or worsen or suicidal ideation is observed, it is recommended to discontinue treatment with PEG-Heberon® and monitor the patient, with appropriate psychiatric treatment.
Patients with the existence or history of serious psychiatric events: if treatment with PEG-Heberon® is considered necessary in patients with or with a history of serious psychiatric events, it should only be started after ensuring an appropriate individualized diagnosis and psychiatric therapeutic treatment. .
Endocrine system: With the use of alpha interferons, abnormalities of thyroid function or worsening of pre-existing thyroid diseases have been observed. Patients with these alterations that cannot be controlled effectively with medication should not start treatment with PEG-Heberon® alone or in combination with ribavirin. Patients who manifest these alterations during treatment and who cannot be controlled with medication, should interrupt therapy.
Autoimmune diseases: the use of different alpha interferon preparations has been associated with an increase in allergic or autoimmune manifestations such as bronchoconstriction, lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis or thyroiditis. Periodic surveillance should be maintained in patients with use of PEG-Heberon® and a history of any of these manifestations. Patients who develop or exacerbate these alterations during treatment and who cannot be controlled by medication, should discontinue therapy.
Eye changes: as with other alpha interferon formulations, retinopathies, including retinal hemorrhages, cotton wool spots, papilledema, optic neuropathy, and retinal artery or vein obstruction have also been observed rarely with pegylated interferon. that can cause a loss of visual ability. Patients who develop these alterations during treatment and who cannot be controlled with medication should discontinue PEG-Heberon® therapy.
Pulmonary disorders: As with other alpha interferon formulations, pulmonary symptoms, including dyspnea, pulmonary infiltrates, pneumonia, and pneumonitis have been reported during treatment with PEG-Heberon®. In the presence of persistent or unexplained pulmonary infiltrates or pulmonary function disorders, treatment should be discontinued.
Dental and periodontal disorders: Dental and periodontal disorders that can lead to tooth loss have been reported in patients who have received treatment with other formulations of pegylated interferon alpha 2b in combination with ribavirin. Dry mouth could also have a detrimental effect on the teeth and oral mucosa during long-term treatment in combination with
PEG-Heberon® alone or in combination with ribavirin should be administered under the supervision of a specialist physician. Treatment may cause adverse reactions of moderate or severe intensity that require a dose reduction, temporary interruption of treatment or permanent suspension.
The main side effects from the use of PEG-Heberon® are similar to those reported for other IFN alpha preparations. These adverse reactions are dose dependent and reversible. Its intensity is generally grade I (does not require treatment) or grade II (yields to symptomatic treatment) of the World Health Organization. If this occurs, appropriate measures should be taken according to the patient’s situation. Although general experience shows that side effects decrease as therapy continues, its continuation or restart in these cases must be carefully monitored.
In a double-blind, crossover, randomized phase I clinical trial that evaluated the biological safety of PEG-Heberon® and recombinant human interferon alfa-2a (Pegasys) in 16 individuals, a similar adverse event profile was obtained for both products. . With the exception of burning at the administration site, the only one with 100% presence for recombinant human interferon alfa-2b versus none for recombinant human interferon alfa-2a, the most frequent adverse events reported by subjects for both formulations were leukopenia. (87.5%), fever (56.3%), thrombocytopenia (56.3%), increased liver enzymes (50%) and asthenia (25%).
The use of PEG-Heberon® in combination with ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C has reported a decrease in leukocyte and hemoglobin levels as the most frequent hematological events (48 and 44% respectively). Clinically, the most common adverse events were asthenia (48%, headache (26%), and burning at the injection site (25%) at the time of PEG-Heberon® administration. Fever, arthralgias, and myalgias were reported in less than 20% of treated patients, most of these events were reported with mild intensity, while none of the moderate or severe were irreversible or had consequences that affected or endangered the integrity of the patient.
The PEG-Heberon® regimen should be established by a physician experienced in treating patients with hepatitis B or C. When PEG-Heberon® is used in combination with ribavirin, professional information on ribavirin should also be consulted.
Chronic hepatitis C
180 μg of PEG-Heberon® is recommended once a week, administered subcutaneously in combination with oral ribavirin, or as monotherapy in cases where ribavirin is contraindicated. In patients with genotypes 1 or 4, the standard daily doses of ribavirin will be administered depending on body weight: 1200 mg for those over 75 kg and 1000 mg for those under 75 kg. In patients with genotypes 2 or 3, 800 mg are administered daily.
The data available for patients infected with genotypes 5 or 6 are limited; therefore, it is recommended that they be treated with a scheme similar to that used for genotypes 1 or 4.
The duration of combination therapy with ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C depends on the viral genotype and the reduction in baseline viral load at weeks 12 and 24 of treatment.
Patients infected with genotypes 1, 4, 5, or 6, with undetectable viral particles at week 12, should be treated for 48 weeks. If there are detectable viral particles at week 12, but a reduction of ≥ 2 log in the baseline viral load, it is recommended to extend the treatment to 72 weeks. When the reduction in baseline viral load at week 12 is less than ≥ 2 log, the patient should permanently discontinue treatment.
Patients infected with genotypes 2 or 3, with undetectable viral particles at week 12 should be treated for 24 weeks. If there are detectable viral particles at week 12, but a reduction of ≥ 2 log in baseline viral load, it is recommended to extend the treatment to 48 weeks. When the reduction in baseline viral load at week 12 is less than 2 log, the patient should definitely discontinue treatment.
Regardless of the viral genotype and the viral load existing at week 12 of treatment, all patients with detectable viral particles at week 24 of treatment must permanently discontinue treatment.
Patients coinfected with hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
The recommended dose of PEG-Heberon® alone or in combination with 800 mg of ribavirin is 180 μg in a weekly subcutaneous injection, regardless of viral genotype.
Prediction of sustained virological response
Early virological response at week 12 of treatment, defined by a decrease in viral load ≥ 2 log or undetectable levels of hepatitis C virus RNA, is an important predictive value of sustained virological response (SVR) at six months after the end of the treatment. The therapeutic consensus for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C recognizes that there is a 98% negative predictive value of SVR in patients with less than 2 log reduction in baseline viral load at week 12 of treatment.
Chronic hepatitis B
The recommended dosage for patients with chronic hepatitis B, both for those with positive HBV and for those with negative HBV, is 180 μg of PEG-Heberon® once a week for 48 weeks, in subcutaneous administration.
As a consequence of adverse effects of moderate or severe intensity, mainly on hematological parameters, it is recommended to reduce the dose of PEG-Heberon® to 135 μg. Sometimes it may be necessary to reduce further to 90 μg or 45 μg or to temporarily interrupt treatment. Once the adverse reactions disappear, consideration should be given to increasing the dose until the initial 180 μg is recovered.
For HIV-coinfected patients, cases of exacerbation of anemia due to ribavirin have been reported when zidovudine is part of HIV treatment, although the exact mechanism has not yet been determined. Concomitant use of ribavirin with zidovudine is not recommended due to the increased risk of anemia. Substitution of zidovudine in combination antiretroviral therapy should be considered if this has been previously established. This is especially important in patients with a history of zidovudine-induced anemia.
There is no other evidence that indicates that treatment with PEG-Heberon® alters and / or modifies the metabolism of other drugs.
There are no studies on the use of PEG-Heberon® in pregnant or lactating women. Therefore, there are no elements that prevent or establish its safe use during pregnancy. Its use should only be under medical prescription and respond to a risk-benefit analysis of the doctor. Breastfeeding should be stopped before starting treatment with PEG-Heberon®.
The influence of PEG-Heberon® on the ability to drive and use machines is small or moderate. If the patient is dizzy, confused, drowsy or fatigued, he should be advised that he should avoid driving vehicles or using machines.
Cases of overdose with similar products have been described, after the administration of 2 injections on consecutive days (instead of weekly doses) up to daily injections for a week (ie, 1,260 μg per week). None of these patients experienced unusual, severe, or treatment-limiting reactions. In clinical studies with similar products, weekly doses reaching 540 μg and 630 μg were administered to patients with renal cell carcinoma and chronic myeloid leukemia, respectively. Dose-limiting toxic reactions, such as fatigue, elevated liver enzymes, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia, are characteristic effects of interferon therapy.